Equivalent dose / tissue effects analysis¶
Module type name (to be used for the module commands):
equivalent_dose
Description¶
The equivalent dose analysis module computes the total (cumulative) “equivalent dose” in the selected volumes. The equivalent dose estimate makes use of radiation Weighting Factors (wR): the user has the choice between the values adopted in ICRP 60, the re-appraisal of the factors given in ICRP 92 and the ones provided in the “2007 Recommendations of the ICRP” (ICRP 103, default in GRAS). The UI Command for this selection is:
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/<moduleName>/setCurve [ICRP60 | ICRP92 | ICRP103]
Particle |
ICRP 60 |
ICRP 92 |
ICRP 103 |
|---|---|---|---|
gamma |
1 |
1 |
1 |
e-, e+, mu+, mu- |
1 |
1 |
1 |
proton |
5 (E>2MeV) |
2 (E>10MeV) |
2 (all energies) |
pi+, pi- |
2 (all energies) |
||
neutron |
ICRP 60 binned function |
ICRP 92 function |
ICRP 103 function |
alpha, ion |
20 |
20 |
20 |
others |
20 |
20 |
20 |
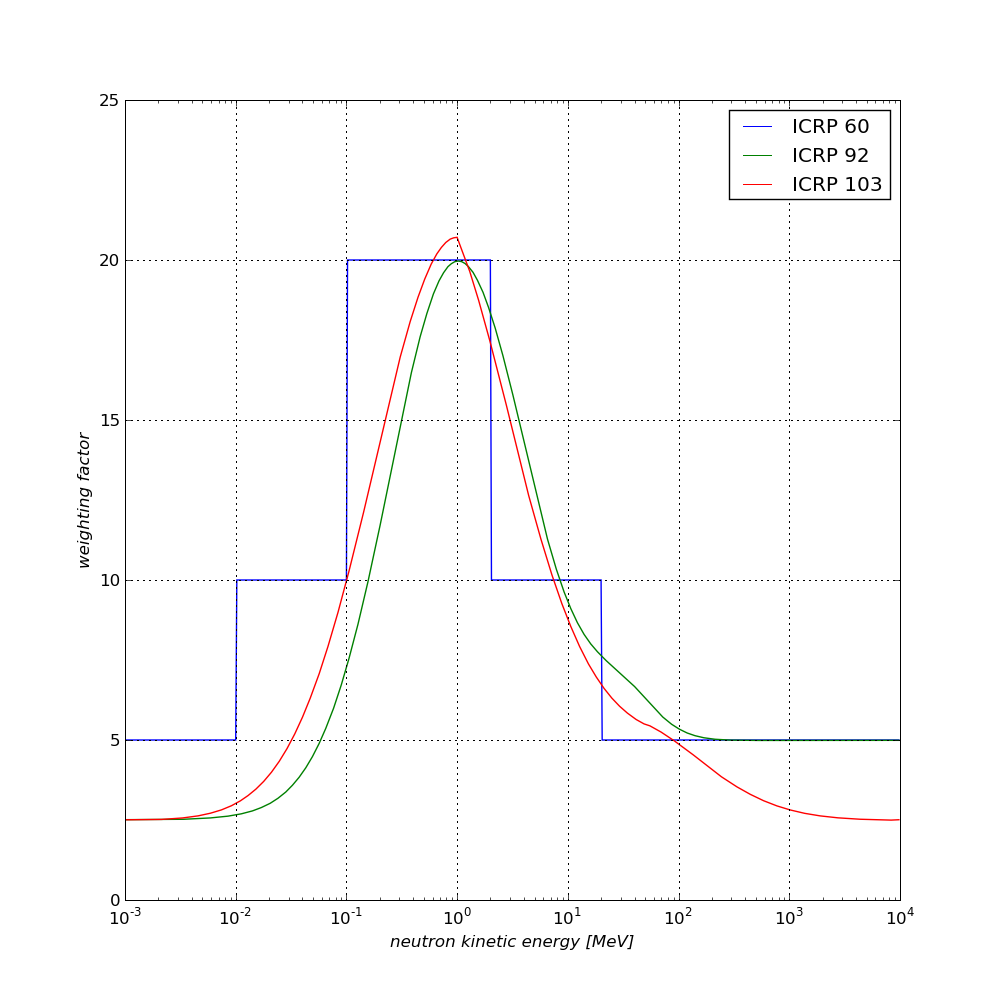
Equivalent dose weighting factors (wF) for neutrons from ICRP 60, ICRP 92, and ICRP 103, as implemented in the GRAS equivalent dose analysis module.¶
When used with the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) weighting
factors as recommended by ICRP draft publication July 2012, ref.
4819-7515-1888, the analysis module can also be used to obtain results
for tissue effects (in units of Gy-eq). The ICRP58 weighting factor
table data was taken from:
ICRP Publication 58 (1989)
Wilson et al., J.Radiat.Res.,43:Suppl.,S103-S106(2002)
NCRP Publication 132
Particle |
Factor |
Energy Range [MeV] |
|---|---|---|
neutron |
5 |
E < 1 |
6 |
1 <= E < 5 |
|
3.5 |
5 <= E |
|
proton |
1.5 |
2 < E |
alpha, ion |
2.5 |
|
others |
1 |
A special technique has been developed in the GRAS application to ensure the correct weighting factor is applied to the dose deposited by the particles (the primaries and the generated secondary products) according to the “incident” particle type: once a weight wR is assigned to a particle, it is then propagated to all its secondary interaction products. The definition of “incident particle” is also not restricted to the primary particle: the user can define as “incident” particles that cross a selected boundary. This is crucial for dosimetry applications in which the primary radiation interacts with a shielding structure before reaching the sensitive target: in this case there is a clear difference between the particles that are “incident” onto the target (astronauts, dosimeters, etc.), which consist of slowed-down primaries and secondary particles, and the primary particle. The user can select the boundary that defines a particle as “incident” module by module, so that analyses can be performed in parallel during the same simulation run on different sensitive target volumes, e.g. whole human body and internal organs.
Script example:
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/addModule eqDoseBody
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/eqDoseBody/addVolume Body
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/eqDoseBody/addVolumeInterface Hall Body
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/eqDoseBody/setCurve ICRP103
/gras/analysis/equivalent_dose/eqDoseBody/setUnit mSv
Available Units¶
The module accepts as units all the G4 units under the “Dose” and “Equivalent Dose” categories. Additional GRAS units that can be used are:
keV/g
MeV/g
MeV/mg
Rad (rad is also accepted, but it is recommended not to be used do distinguish it from the “Angle” unit)
Gy-eq
Sv
mSv
pGy
Specific Module commands¶
The Module is based on the Generic Factors Analysis module, so the commands specified therein are available to this module also.
Output¶
The Module is based on the Generic Factors Analysis module, so the output information specified therein is available to this module also.
The GFMtype is EqDose.
GRAS/trunk/r2242
